No. 10 Effect of Manuka honey ① <Antimicrobial activity>
Manuka honey?
Manuka honey of New Zealand
Manuka honey is produced by bees which gather nectar from the Manuka bush (Leptospermum scoparium), one of the indigenous New Zealand Myrtaceae.
It contains anti-bacterial compound, Methylglyoxal (MGO) at high concentration and research results have shown that it possesses strong antibacterial activity which no other honeys possess against pathogens like Helicobacter pylori or Streptococcus mutans.

Antimicrobial activity of Manuka honey
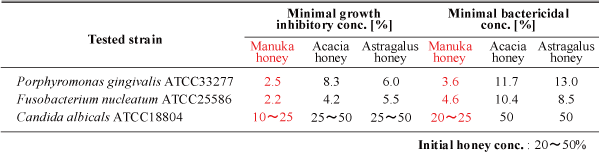
Antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms
Antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori were isolated from biopsy samples taken from the margin of gastric ulcers.
The antibacterial activity of manuka honey against five isolates of Helicobacter pylori assessed by an agar well diffusion assay.
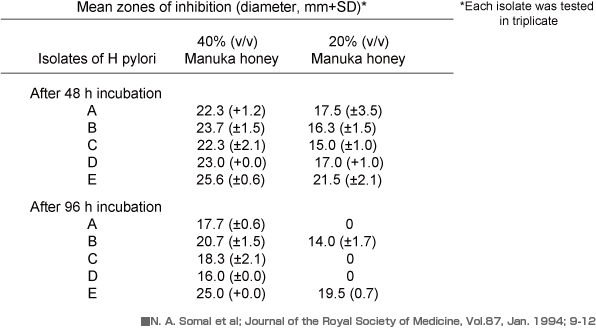
The diameter of the clear zones around the wells was measured.
Some of the isolates were able to grow at this lower concentration after prolonged incubation allowed the antibacterial activity to become lowered by diffusion, but it can be seen that manuka honey has a good antibacterial activity against all five isolates even when diluted to 20%.
Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration of manuka honey against seven isolates of Helicobacter pylori. The results are shown as growth observed after 72 h incubation of the isolates on plates with various concentrations of honey incorporated in the agar.
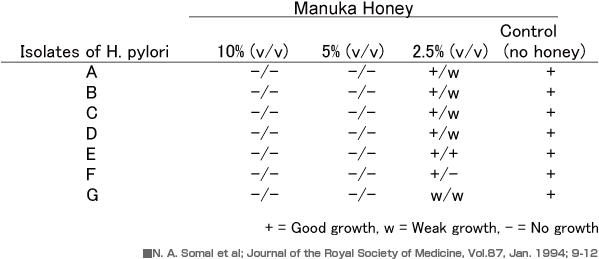
It can be seen that complete inhibition of growth of all seven isolates tested, over an incubation period of 72 h, was achieved by the presence of manuka honey at 5% of its full strength; partial inhibition of some isolates was achieved at 2.5%.
The effects of the combinations of ingredients on the growth of the bacteria
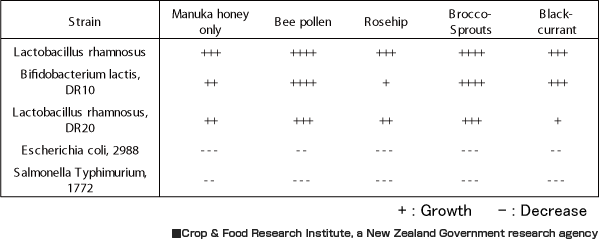
Manuka honey increased probiotic growth and decreased pathogen growth in a dose-dependent manner.
