No. 53 Influence of Tocotrienol-γ-Cyclodextrin complex in Various Stress Tolerance of Caenorhabditis elegans
This research was reported in 29th Cyclodextrin Symposium (Hoshi Univ., Tokyo, Sep. 6~7, 2012).
Background
Our company have an attract attention technology in functional food and personal care fields which raises the water solubility, stability and bioavailability of a functional ingredient by using the inclusion property of cyclodextrin (CD).
Recently, we focused "Tocotrienol" as a notable anti-aging ingredient and succeeded in the enhancement of its thermal stability and bioavailability by inclusion with γ-CD (* please refer to the newest result of research "38th" of our homepage for details.). We believe those results showed that "Tocotrienol-γ-CD complex" is useful as functional health food and cosmetics materials.
In this research, the prolongevity effects of Tocotrienol-γ-CD complex supplementation in Caenorhabditis elegans stimulated with various stress were explored.
Structures of tocotrienols
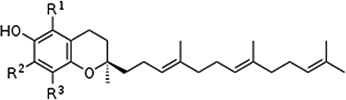
Appeal points of tocotrienol
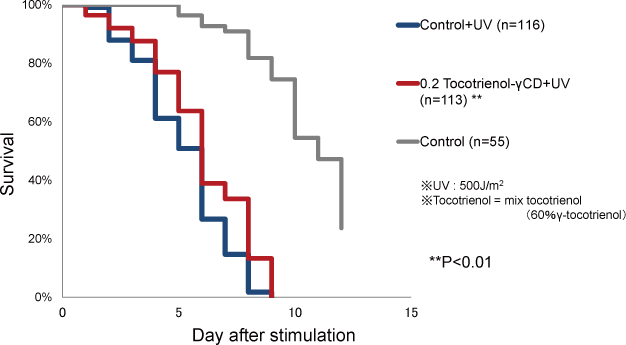
Stress tolerance of C. elegans was enhanced by supplementation of tocotrienol-γ-CD complex under UV stress.
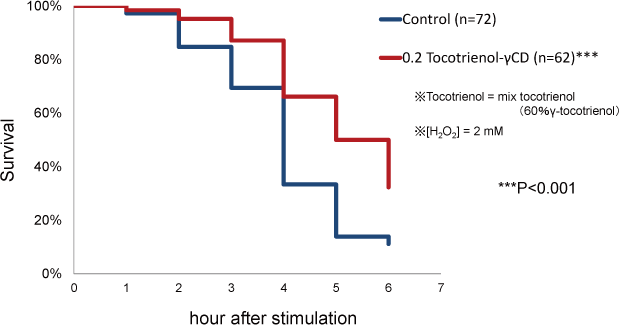
Stress tolerance of C. elegans was enhanced by supplementation of tocotrienol-γ-CD complex under hydrogen peroxide stress.
The prolongevity effects among tocotrienol isomers in C. elegans were compared.
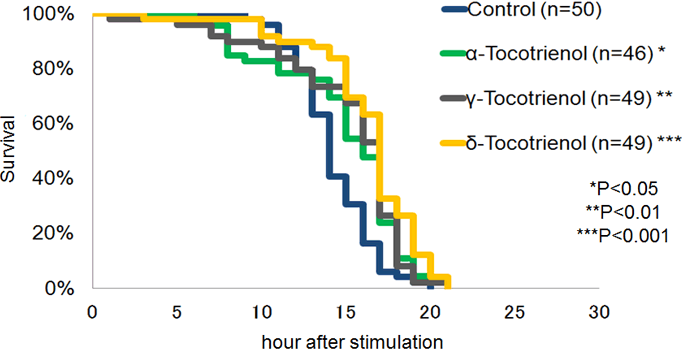
- All isomers of tocotrienol-γ-CD showed prolongevity effects in C. elegans.
- δ-tocotrienol-γ-CD was the most effective in all isomers.
Conclusion
- Stress tolerances of C. elegans were enhanced by supplementation of tocotrienol-γ-CD complex under UV or hydrogen peroxide stress.
- Each isoform of α-, γ-, or δ-tocotrienol-γ-CD complex was individually administered to C. elegans as a dietary supplement. The lifespan of worms supplemented with δ-tocotrienol-γ-CD was the most prolonged compared to that of worms supplemented with other isoforms.
