No. 82 Study on a novel dehydration condensation reagent combining monochlorotriazinyl β-cyclodextrin and N-methylmorpholine
Summary
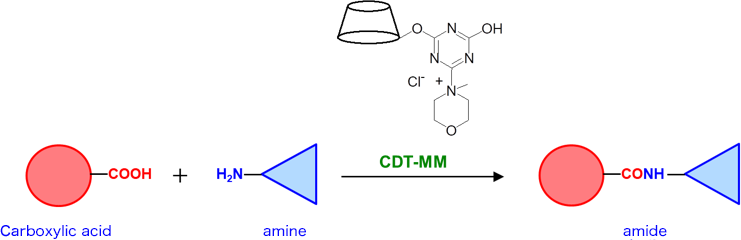
The amide bond exists in various organic compounds such as biomolecules, pharmaceuticals and synthetic resins. Amide compounds are very often synthesized in organic synthesis. Condensation reagents are often used in the synthesis of amide compounds. DMT-MM, synthesized from 2-chloro-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine (CDMT) and N-methylmorpholine (NMM), is known as a superior condensation reagent because it allows the reaction to proceed under milder conditions than carbodiimide-based condensation reagents and can be used in water1, 2).
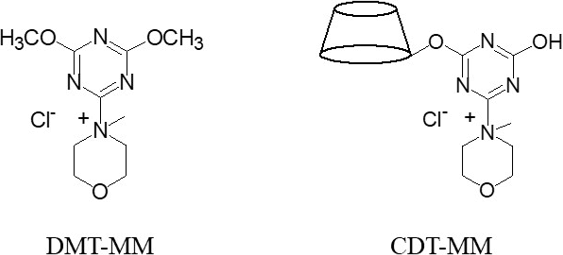
On the other hand, monochlorotriazinyl β-cyclodextrin (MCT-β-CD), industrially produced, has been used as a reactive CD for the preparation of various functionalizing fibers3). CDT-MM is obtained by the reaction of chlorotriazinyl group of MCT-β-CD with NMM. CDT-MM can be regarded as a CD having DMT-MM. In this study, we investigated the use of CDT-MM as a condensation reagent (Fig. 1).
Experimental
Preparation of CDT-MM
After dissolving MCT-β-CD in water, 5 molar equivalents of NMM were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 46 hours to obtain a CDT-MM aqueous solution.
Application of CDT-MM for condensation reaction
- Condensation reaction of aromatic carboxylic acid and amine
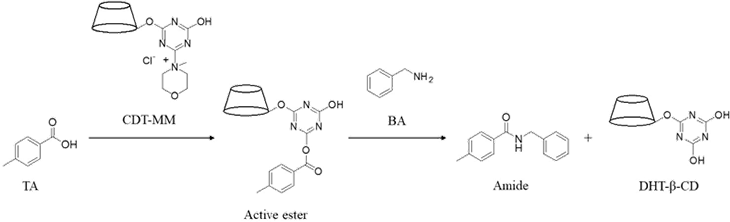
Toluic acid (TA) and benzylamine (BA) were added to the CDT-MM aqueous solution in this order, and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature and pH8. Instead of the CDT-MM aqueous solution, MCT-β-CD aqueous solution, NMM aqueous solution and a mixed aqueous solution of dihydroxytriazinyl β-CD (DHT-β-CD) and NMM were used as negative controls for the evaluations of condensation reaction by the same procedure. - Condensation reaction of linear fatty acid and amine
Using CDT-MM, the condensation reactions of various linear fatty acids (acetic acid, propionic acid, hexanoic acid, octanoic acid) with BA were examined in the same manner as above.
Results and Discussion
When TA and BA were reacted for 2 hours in the presence of CDT-MM as a condensation reagent in water, a spot of the desired amide was observed on thin layer chromatography. However, as negative controls, when MCT-β-CD, NMM or a mixture DHT-β-CD and NMM was used instead of CDT-MM, the amide spot was not observed.
This indicated that CDT-MM could be used as a condensation reagent in the synthesis of amides (Scheme 1). Next, when four kinds of linear fatty acids were used as acids to react with BA, the corresponding amide was formed only with hexanoic acid. Thus, it was shown that CDT-MM possess chain length selectivity when linear fatty acids were used as substrates. It was thought to be due to the influence of inclusion property of CDT-MM. It was also confirmed that CDT-MM maintains its function even after powderized from an aqueous solution.
Conclusion
In this study, it was confirmed that CDT-MM can be used as a condensation reagent.
In the future, CDT-MM is expected to be applied for the synthesis of various amide compounds as a new condensation reagent having the inclusion ability of CD.
Reference
1) M. Kunishima, K. Terao et al., Tetrahedron Letters, 40, 5327-5330 (1999).
2) M. Kunishima, K. Terao et al., Tetrahedron, 57, 1551-1558 (2001).
3) T. Akita et al., Science and industry, 71(5), 124 (2018)
