No. 44 Defining the mechanism of reduced blood cholesterol by α-cyclodextrin supplementation.
This research was reported in 29th Cyclodextrin Symposium (Hoshi Univ., Tokyo, Sep. 6~7, 2012).
α-CD supplementation - previous report -

Whereas α-CD could not bind to cholesterol, it has been reported that blood cholesterol level was reduced by α-CD supplementation in mice.
↓
α-CD can inhibit cholesterol absorption indirectly ?
Small-intestinal absorption of lipids
It is important for lipid absorption that lipids are mixed with bile acid micelle and dissolved in intestinal juice.
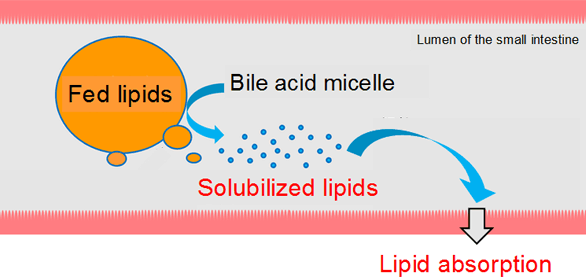
H. Yano, et al. (2009).
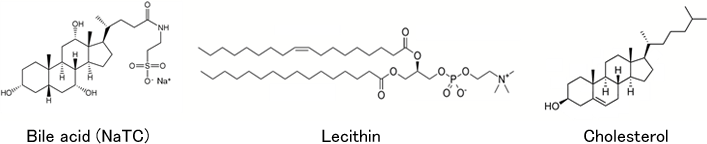
Constituents of bile
| bile | |
| Bile acid (mM) | 72.1 (68%) |
| Lecithin (phospholipids) (mM) | 25.8 (23%) |
| Cholesterol (mM) | 8.1 (7.6%) |
| water (%) | 84 |
α-CD can bind only lecithin in bile constituents.
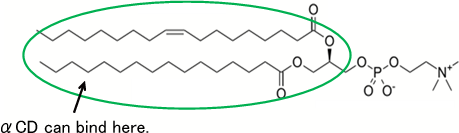
A hypothesis
Fed α-CD binds lecithin of bile acid micelle in small-intestine.
↓
Lipid solubilization capacity of bile acid micelle should be lower.
↓
α-CD can inhibit cholesterol absorption indirectly.
Study points
The effects of α-CD to artificial intestinal juice
- The interaction between α-CD and lecithin
- The solubility of cholesterol to artificial intestinal juice in the presence of α-CD.
were explored.
Artificial intestinal juice
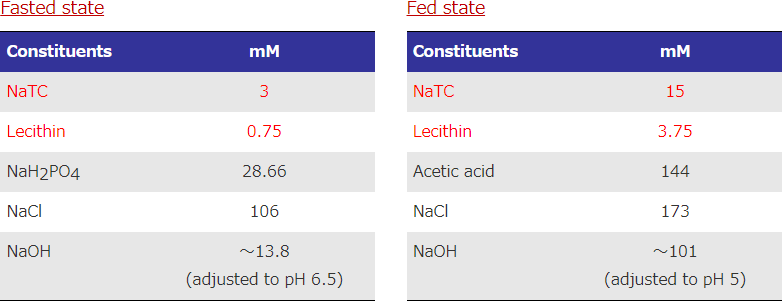
M. Vertzoni, et al. (2004)
Fig. 1. Turbidity of artificial intestinal juice in the presence of α-CD
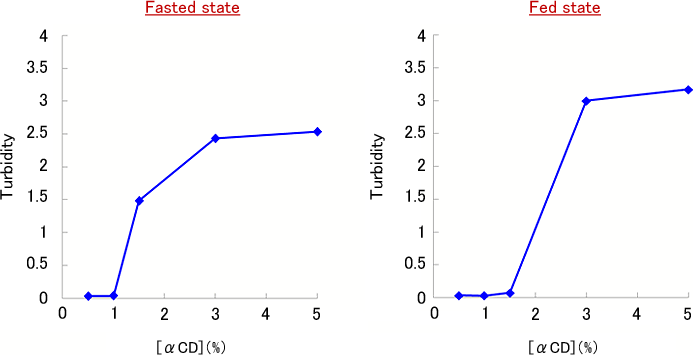
Increase of turbidity was observed by the addition of α-CD to artificial intestinal juice.
Fig. 2. the interaction between α-CD and lecithin.
artificial intestinal juice in the presence of α-CD (3%)

White precipitation was formed in the case of coexistence of α-CD and lecithin.
→ α-CD can bind to lecithin selectively in artificial intestinal juice. (The precipitation was α-CD-lecithin complex.)
Fig. 3. Aqueous solubility of cholesterol in artificial intestinal juice.
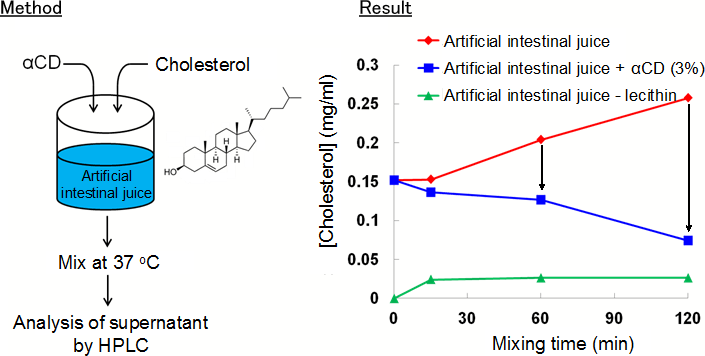
Decrease of aqueous solubility of cholesterol in artificail intestinal juice was observed in the presence of α-CD.
Conclusion
Lecithin was precipitated from bile acid micelle by complexation with α-CD.
Therefore, aqueous solubility of cholesterol was lowered in artificial intestinal juice without lecithin.
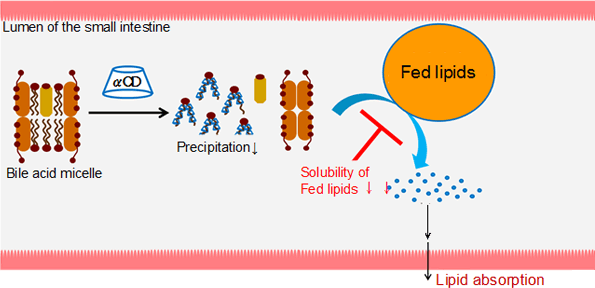
From these results, we clarified one of the mechanisms of the reducing effect of blood cholesterol level by α-CD supplementation.
