No. 59 Defining the mechanism of reduced blood cholesterol by α-cyclodextrin supplementation ②
This research was reported in 30th Cyclodextrin Symposium (Kumamoto, Sep. 12~13, 2013).
Background
Our company has an attract attention technology in functional food and personal care fields which raises the water solubility, stability and bioavailability of functional ingredients by using the inclusion property of cyclodextrin (CD).
Because of its high water solubility and non-digestible property, α-CD can be taken as a water-soluble dietary fiber. Indeed, daily feed intake of α-CD shows some anti-metabolic syndrome effects, improvements of the intestinal environment and anti-allergy effect. We also reported some interesting results supporting those effects (* please refer to the newest result of research "16th", "42th", "44th" and "50th" of our homepage for details.).
In this study, we report a new knowledge of α-CD function on the mechanism of reduced blood cholesterol level by α-CD supplementation.
Functions of α-CD (human trial)
- Anti-metabolic syndrome
Lowering effect of fat and cholesterol
Inhibition effect against an elevation in blood glucose level - Regulation of intestinal functions
- Anti-allergy
Atopic dermatitis, Cedar pollen allergy, Asthma
Our previous study
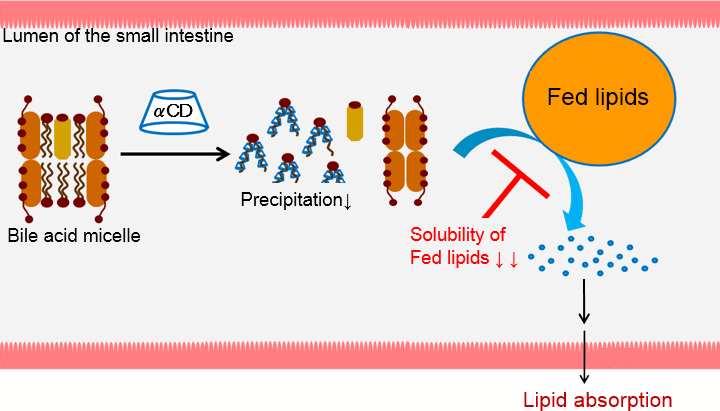
Lecithin was precipitated from bile acid micelle by complexation with α-CD.
Therefore, aqueous solubility of cholesterol was lowered in artificial intestinal juice due to reduced lecithin content.
↓
We clarified one of the mechanisms of the reducing effect of blood cholesterol level by α-CD supplementation.
Further studies are continued for understanding the details of the mechanisms.
In this study
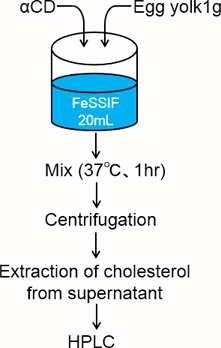
Cholesterol reagent commercially available as model fat was used in previous study.
In this study, egg yolk was used as model food.
And, solubility of cholesterol from egg yolk was evaluated in the presence of α-CD in artificial intestinal juice.
Artificial intestinal juice (FeSSIF)
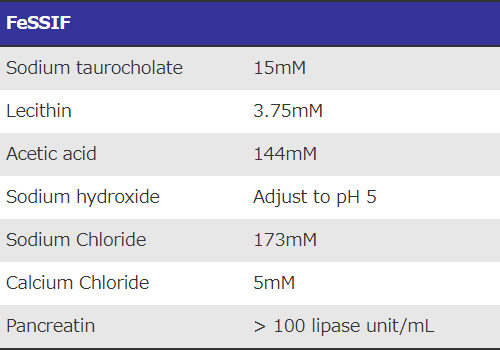
M. Vertzoni, et al. (2004)
E. Jantratid, et al. (2008)
Experiment
Result
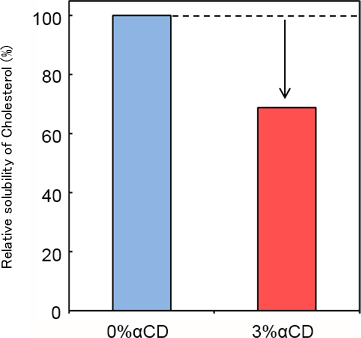
Decrease of aqueous solubility of egg yolk cholesterol in FeSSIF was observed in the presence of α-CD.
Colclusion
α-CD could be a potent inhibitor of the absorption of cholesterol from food matrix by interaction with lecithin in intestinal juice.
This mechanism have not be reported in other dietary fibers. So, we recommend for daily intake of α-CD as a unique and effective dietary fiber with many benefits.
