No. 78 Defining a mechanism of selective decreasing effect on serum trans fatty acid by α-CD supplementation
This research was done through collaboration with Kobe University and reported in the joint conference of 8th Asian Cyclodextrin Conference and 32th Cyclodextrin Symposium (Kumamoto, May 14~16, 2015).
Background
Our company has an attract attention technology in functional food and personal care fields which raises the water solubility, stability and bioavailability of functional ingredients by using the inclusion property of cyclodextrin (CD).
Because of its high water solubility and non-digestible property, α-CD can be taken as a water-soluble dietary fiber. Indeed, daily feed intake of α-CD shows some anti-metabolic syndrome effects, improvements of the intestinal environment and anti-allergy effect. We also reported some interesting results supporting those effects (* please refer to the newest result of research "16th", "42th", "44th" and "50th" of our homepage for details.).
In this study, we report a new knowledge of α-CD function on the mechanism of selective decreasing effect on serum trans fatty acids by α-CD supplementation.
Functions of α-CD (human trial)
- Anti-metabolic syndrome
Lowering effect of fat and cholesterol
Inhibition effect against an elevation in blood glucose level - Regulation of intestinal functions
- Anti-allergy
Atopic dermatitis, Cedar pollen allergy, Asthma
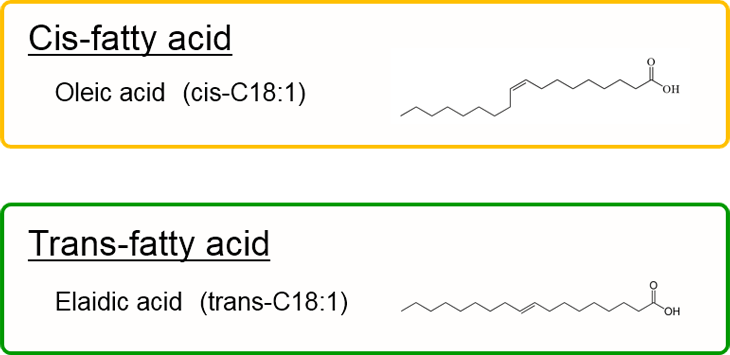
Trans fatty acid
Trans fatty acid is a kind of unsaturated fatty acid generated in the production process of margarine. Natural abundance of trans fatty acid is very low. And it is well known that having too much trans fatty acid causes increase of risk of heart disease. So, we have to pay attention to take much trans fatty acids.
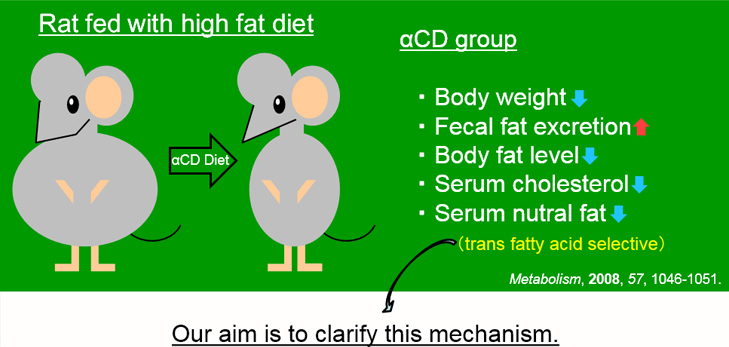
Under such background, selective decreasing effect on serum trans fatty acid by α-CD supplementation in rats has been reported.
Selective decreasing effect on serum trans fatty acids by α-CD supplementation.
Fatty acids
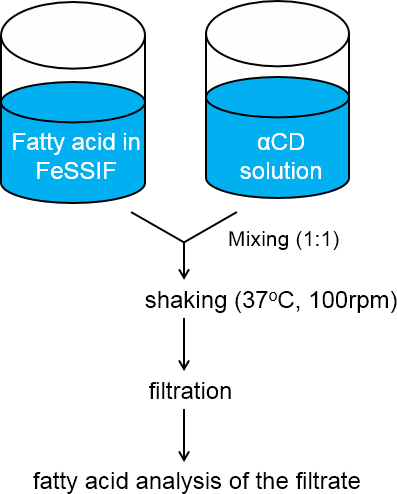
Experiment
The effects of α-CD to solubilities of fatty acids in fed-state simulated intestinal fluid (FeSSIF) were explored.
Result. Decreasing effects of α-CD on the fatty acid solubility (trans vs cis)
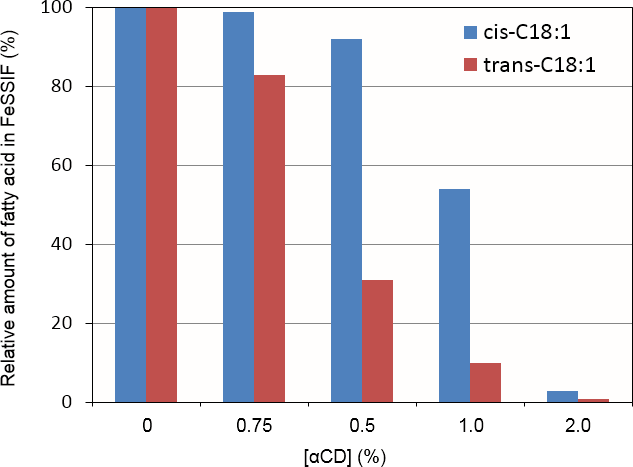
α-CD decreased the solubility of trans-fatty acid (trans-C18:1) more effectively than that of cis-fatty acid (cis-C18:1).
Discussion
It is well known that absorption of fatty acids is achieved by dissolving in the small intestinal fluid.
Hence, from these results, we consider that α-CD may absorb fatty acids selectively by the decreasing the solubilities of fatty acids in the small intestinal fluid.
→ In the present study, we clarified the mechanisms of selective decreasing effect on serum trans fatty acid by α-CD supplementation.
